what stance do firms who do as little as possible to solve social or environmental problems take
3 Special Stakeholders: Society, the Surround, and Regime
Sustainability: Business and the Environment
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, y'all volition be able to:
- Explain the concept of earth jurisprudence
- Evaluate the claim that sustainability benefits both concern and the environment
- Identify and describe initiatives that try to regulate pollution or encourage businesses to prefer make clean energy sources
Public concern for the natural environment is a relatively new phenomenon, dating from the 1960s and Rachel Carson'due south seminal book Silent Bound, published in 1962. In 1992, Cormac Cullinan'due south Wild Law proposed "world justice" or "earth jurisprudence," a concept underlying the law'due south ability to protect the environment and effectively regulate businesses that pollute. The preoccupation with business success through investment in corporations, in contrast, is a much older concept, dating back at to the lowest degree to the creation of the British East Republic of india Company in 1600, and the widespread emergence of the corporation in Europe in the 1700s. If you were a business owner, would you be willing to spend visitor resources on environmental issues, fifty-fifty if not required to practice and then by law? If so, would yous be able to justify your actions to shareholders and investment analysts as smart business organization decisions?
Ecology Justice
If a business activity harms the environment, what rights does the environment have to fight back? Corporations, although a form of concern entity, are really considered persons in the eyes of the police force. Formally, corporate personhood, a concept nosotros touched on in the preceding section, is the legal doctrine holding that a corporation, separate and apart from the people who are its owners and managers, has some of the aforementioned legal rights and responsibilities enjoyed past natural persons (physical humans), based on an interpretation of the word "person" in the Fourteenth Amendment.
The by and large accepted ramble basis for allowing corporations to assert that they have rights like to those of a natural person is that they are organizations of people who should not be deprived of their rights only because they act collectively. Thus, treating corporations as persons who have legal rights allows them to enter into contracts with other parties and to sue and be sued in a courtroom of police force, forth with numerous other legal rights. Before and after the Supreme Court'south ruling in Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission (2010), which upheld the First Subpoena gratuitous-speech rights of corporations, at that place take been numerous challenges to the concept of corporate personhood; however, none have been successful. Thus, U.S. law considers corporations to exist persons with rights protected under primal constitutional amendments, regulations, and case police, also as responsibilities under the police force, but every bit human persons have.
A question that logically springs from judicial interpretations of corporate personhood is whether the surroundings should enjoy similar legal status. Should the environment be considered the legal equivalent of a person, able to sue a business that pollutes it? Should environmental advocates have been able to file a lawsuit against BP (formerly British Petroleum) on behalf of the unabridged Gulf of United mexican states for harm created by the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill (discussed in more detail in the government regulation section of this affiliate), which, at five million barrels, was x times larger than the famous Exxon Valdez spill and remains the largest and most widespread ocean oil spill in the history of the global petroleum industry? Furthermore, the Deepwater Horizon spill affected non only thousands of businesses and people, but also the entirety of the Gulf of United mexican states, which will suffer harm for years to come. Should the Gulf of Mexico have legal continuing to sue, just similar a person?
While U.S. jurisprudence has not notwithstanding officially recognized the concept that Globe has legal rights, in that location are examples of progress. Ecuador is now the first state to officially recognize the concept.
The country rewrote its Constitution in 2008, and it includes a section entitled "Rights for Nature." It recognizes nature's right to exist, and people have the legal say-so to enforce these rights on behalf of the ecosystem, which tin can itself be named as a litigant in a lawsuit.
Earth jurisprudence is an estimation of constabulary and governance based on the belief that gild will be sustainable but if we recognize the legal rights of World equally if it were a person. Advocates of earth jurisprudence assert that there is legal precedent for this position. As pointed out earlier in this affiliate, information technology is non only natural persons who have legal rights, but too corporations, which are artificial entities. Our legal organisation also recognizes the rights of animals and has for several decades. Co-ordinate to earth jurisprudence advocates, officially recognizing the legal status of the environment is necessary to preserving a salubrious planet for time to come generations, in particular because of the trouble of "invisible pollution."
Businesses that pollute the environment often hide what they are doing in society to avoid getting caught and facing economical, legal, or social consequences. The only witness may be Globe itself, which experiences the harmful impact of their invisible deportment. For example, as revealed in a contempo report,
companies all over the world take for years been secretly called-for toxic materials, such as carbon dioxide, at night. A company that needs to dump a toxic substance unremarkably has three choices: dispose of it properly at a safe facility, recycle and reuse it, or secretly dump information technology. At that place is no doubt that dumping is the easiest and cheapest option for most businesses.
As another example, approximately twenty-five meg people board cruise ships every yr, and as a result, cruise ships dump 1 billion gallons (three.8 billion liters) of sewage into the oceans annually, commonly at night and then no one sees or smells it. Friends of the Earth, a nongovernmental system (NGO) concerned with environmental issues, used data from the U.S. Ecology Protection Agency (EPA) to calculate this figure.
The sewage dumped into the sea is full of toxins, including heavy metals, pathogens, bacteria, viruses, and pharmaceutical drugs ((Figure)). When invisibly released near coasts, this untreated sewage tin can kill marine animals, contaminate seafood, and sicken swimmers, and no one registers the damage except the body of water itself. Many believe the environment should have the right not to be secretly polluted in the expressionless of night, and Earth should have rights at to the lowest degree equal to those of corporations.
A warning in Honolulu regarding the damage done by ocean dumping. (credit: "No Dumping – Drains to Body of water" by Daniel Ramirez/Wikimedia Commons, CC By 2.0)

Cormac Cullinan, an environmental attorney, author, and leading proponent of earth jurisprudence, often collaborates with other environmental advocates such as Thomas Berry, an eco-theologian, scholar, and writer. Cullinan, Berry, and others have written extensively about the important legal tenets of earth jurisprudence; however, it is not a legal doctrine officially adopted past the United States or any of its states to date. The concept of earth justice is tied indirectly to the economical theory of the "tragedy of the eatables," a phrase derived from British economist William Forster Lloyd, who, in the mid-nineteenth century, used a hypothetical example of unregulated grazing on common land to explain the human tendency to human activity independently, putting self-involvement outset, without regard for the mutual adept of all users. The theory was later popularized by ecologist and philosopher Garrett Hardin, who tied it directly to environmental bug. In other words, when information technology comes to natural resources, the tragedy of the eatables holds that people generally apply equally much of a free resource as they desire, without regard for the needs of others or for the long-term environmental furnishings. Equally a way of combating the tragedy of the commons, Cullinan and others take written about the concept of earth justice,
which includes the following tenets:
"The Earth and all living things that constitute it have cardinal rights, including the right to exist, to accept a habitat or a place to be.
Humans must adjust their legal, political, economic, and social systems to be consequent with the primal laws or principles that govern how the universe functions.
Human acts, including acts by businesses that infringe on the fundamental rights of other living things violate fundamental principles and are therefore illegitimate and unlawful."
The concept of earth justice relies heavily on Garrett Hardin'southward word of the tragedy of the commons in Science in 1968.
This classic analysis of the environmental dilemma describes how, from colonial times, Americans regarded the natural environment as something to be used for their own farming and concern ends. Overuse, however, results in the inevitable depletion of resources that negatively affects the environment, so that it eventually loses all value.
Today, supporters of the environment assert that government has both a right and an obligation to ensure that businesses do not overuse whatever resource, and to mandate adequate ecology protection when doing so. In addition, some form of fee may exist collected for using upwards a natural resource, such equally severance taxes imposed on the removal of nonrenewable resource like oil and gas, or deposits required for possible cleanup costs subsequently projects have been abandoned. Every bit role of the growing acceptance of the concept of globe justice, several nonprofit educational organizations and NGOs have become agile in both lobbying and ecology litigation. 1 such arrangement is the Center for Earth Jurisprudence (housed at the Barry School of Law in Orlando), a nonprofit group that conducts research in this area.
The post-obit video describing the Center for World Jurisprudence discusses back up for laws that legally protect the sustainability of life and health on Globe, focusing upon the springs and other waters of Florida.
Why Sustainability Is Expert for Business organisation
The notion that the environs should be treated as a person is relatively new. Simply given the prominence of the environmental movement worldwide, no well-managed business today should be conducted without an awareness of the tenuous residue between the health of the environs and corporate profits. It is quite simply good business practice for executives to exist aware that their enterprise's long-term sustainability, and indeed its profitability, depend profoundly on their safeguarding the natural environs. Ignoring this interrelationship between business and the environment not only elicits public condemnation and the attention of lawmakers who heed to their constituents, but it also risks destroying the viability of the companies themselves. Virtually all businesses depend on natural resources in i fashion or some other.
Progressive corporate managers recognize the multifaceted nature of sustainability—a long-term approach to business organisation activity, environmental responsibility, and societal impact. Sustainability affects not only the environment simply also other stakeholders, including employees, the community, politics, police force, science, and philosophy. A successful sustainability program thus requires the commitment of every office of the company. For example, engineers are designing manufacturing and production processes to run into the demands of companies dedicated to sustainability, and the idea of visitor-wide sustainability is now mainstream. Many of the largest companies in the world see sustainability every bit an important part of their future survivability.
The Global 100 and Sustainability's Strategic Worth
Corporate Knights is a Canadian research and publishing company that compiles an annual list called the Global 100, identifying the world's most sustainable companies.
The 2018 edition of the list, presented at the Globe Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, shows that an increasing number of major multinational companies have sustainability seriously, including many U.S. businesses. The highest-ranking U.S. visitor is applied science behemothic Cisco, which ranks seventh on the Global 100 list.
Other U.Due south. companies in the top twenty-five include Autodesk, Merck, and McCormick & Co. The countries with the all-time representation on the listing are primarily from North America and Western Europe: the United States (xviii), France (15), the United Kingdom (10), Germany (7), Brazil (v), Finland (five), and Sweden (v).
Y'all may await that companies dedicated to sustainability would be less assisting in the long run equally they face up additional costs. In fact, data from the Global 100's return on investment shows this is not the example. Let'south examine the evidence. If an investor had put $250 in Global 100 companies in 2005, information technology would have been worth $580 in 2015, compared to $520 for the aforementioned amount invested in a typical alphabetize fund. The Global 100's cumulative return on high-sustainability firms is most 25 percent higher than a traditional investment.
Cisco Systems, number seven on the global list, is a good example of how green procurement and sustainable sourcing have become a regular function of the supply chain. At Cisco, according to a acme-level supply chain executive, "nosotros take seriously the responsibility of delivering products in an ethical and environmentally responsible manner."
Cisco relies on its Supplier Code of Conduct to set standards for suppliers so they follow fair labor practices, ensure safe working conditions, and reduce their carbon footprint, the amount of carbon dioxide and other carbon compounds released by the consumption of fossil fuels, which tin be measured quantitatively (run into the link below). Cisco is in the process of embedding sustainability into supply chain management at all levels.
Do you know what your carbon footprint is? This personal footprint calculator allows you to find out where yous stand up.
Another company dedicated to sustainability is Siemens, which was ranked number ix on the 2018 list. Siemens is a multinational industrial conglomerate headquartered in Frg, whose businesses range from ability plants to electrical systems and equipment in the medical field and high-tech electronics. Siemens was rated the most energy-efficient house in its sector, because information technology produced more dollars in acquirement per kilowatt used than any other industrial corporation. This is a standard technique to gauge efficiency and demonstrates that Siemens has a low carbon footprint for a visitor in the industries in which it operates. The commitment of Siemens to sustainability is farther demonstrated by its decision to manufacture and sell more environmentally friendly infrastructure products such equally green heating and air conditioning systems.
Cisco and Siemens testify that businesses across the world are starting to understand that for a supply chain to be sustainable, companies and their vendors must exist partners in a clean and safe environment. Exercise businesses simply pay lip service to ecology issues while using all available natural resources to make as much money as they tin can in the present, or are they actually committed to sustainability? There is abundant evidence that sustainability has become a policy adopted by businesses for financial reasons, not simply public relations.
McKinsey & Visitor is one of the world's largest management consulting firms and a leader in the utilise of data analytics, both qualitative and quantitative, to evaluate direction decisions. McKinsey conducts periodic surveys of companies around the globe on matters of importance to corporate leaders. In the 2010 survey, 76 percentage of executives agreed that sustainability provides shareholders long-term value, and in the 2014 survey, entitled "Sustainability'south Strategic Worth," the information indicated that many companies consider cost savings to be the number-i reason for adopting such policies. Price cutting, improved operations, and efficiency were indicated as the primary reasons for adopting sustainability policies by over ane-tertiary of all companies (36%).
Other major studies accept demonstrated similar results. Grant Thornton is a leading global accounting and consulting firm. Its 2014 report on CSR showed that the top reason companies cite for moving towards more environmentally responsible business organisation practices is fiscal savings. Grant Thornton conducted more than two,500 interviews with clients and concern executives in approximately 30-five countries to discover why companies are making a commitment to sustainable practices. The study found that cost management was the key reason for sustainability (67%).
A specific example is Dell Computers, headquartered exterior Austin, Texas, and with operations all over the world. The "Dell Legacy of Good Plan" has prepare a goal to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from all facilities and operations by l percent by the year 2020, along with several other environmental goals. As part of this overall plan, Dell created the Connected Workplace, a flex-piece of work program assuasive alternative arrangements such as variable work hours to avoid rush hour, full- or part-time piece of work at habitation flexibility, and job sharing. This sustainability initiative helps the visitor avoid virtually seven thousand metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions, and, straight related to the financial benefit of sustainability, information technology saves the company approximately $12 million per year.
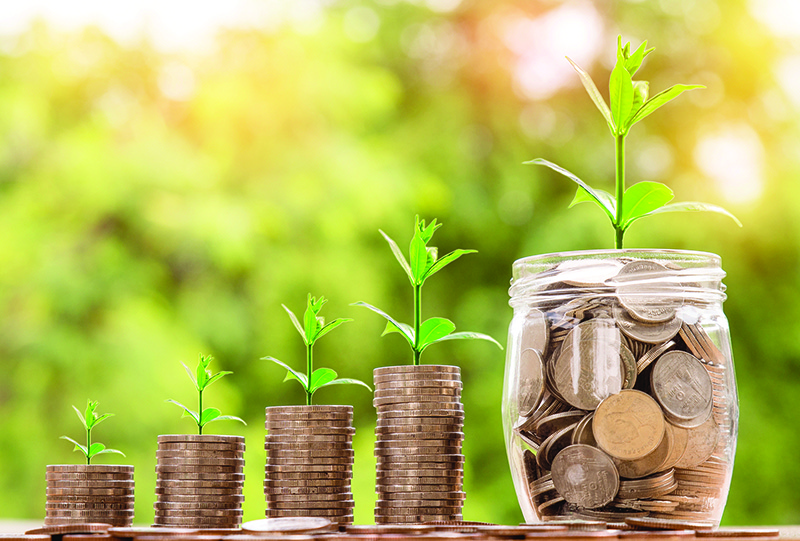
Still, adopting sustainability policies may require a long-term outlook. A recent commodity in the Harvard Business Review discussed the issue of sustainability and how information technology can create existent price savings ((Figure)). "It's difficult for companies to recognize that sustainable product can be less expensive. That'southward in part because they have to fundamentally change the way they think near lowering costs, taking a leap of faith . . . that initial investments made in more-costly materials and methods volition lead to greater savings downwardly the road. It may also crave a willingness to buck conventional financial wisdom by focusing not on reducing the cost of each part but on increasing the efficiency of the organization as a whole."
Sustainability can create long-term toll savings for companies. (credit: work by Nattanan Kanchanaprat/Pixabay, CC0)

Sustainability Standards
The International System for Standardization, or ISO, is an independent NGO and the world'southward largest developer of voluntary international business standards. More than twenty thousand ISO standards now cover matters such equally sustainability, manufactured products, engineering science, food, agriculture, and even healthcare. The adoption and apply of these standards past companies is voluntary, only they are widely accepted, and following ISO certification guidelines results in the creation of products and services that are clean, safety, reliable, and fabricated past workers who enjoy some degree of protection from workplace hazards.
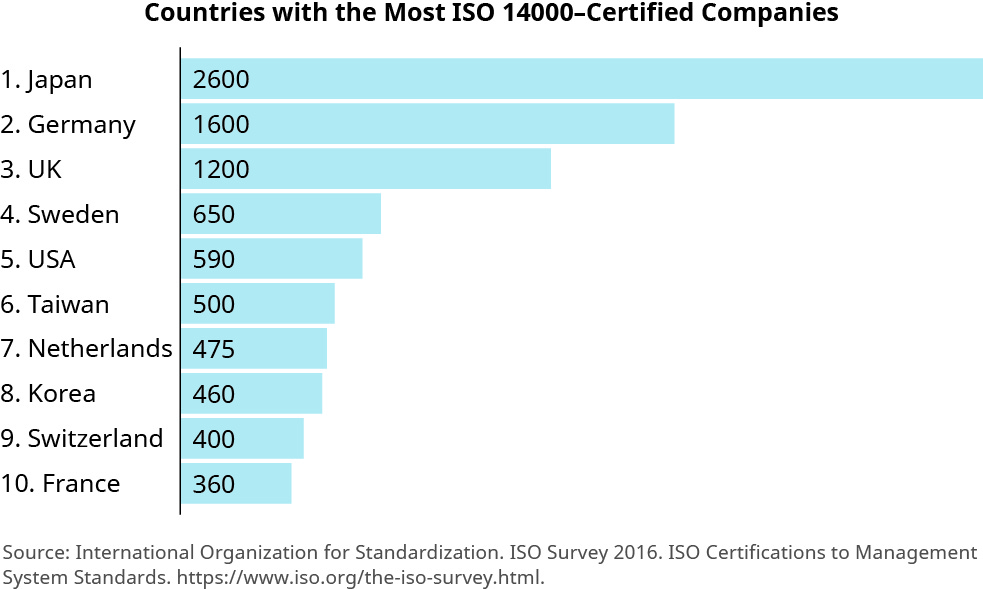
In the environmental expanse, the ISO 14000 serial of standards promotes effective environmental direction systems in business organizations by providing cost-effective tools that make use of all-time practices for ecology direction. These standards were developed in the 1990s and updated in 2015; they cover everything from the eco-pattern (ISO 14006) of factories and buildings to environmental labels (ISO 14020) to limits on the release of greenhouse gasses (ISO 14064). While their adoption is withal voluntary, a growing number of countries allow only ISO 14000-certified companies to bid on public regime contracts, and the same is true of some individual-sector companies ((Figure)).
According to recent reports, shut to xv thousand companies worldwide take chosen to be ISO 14000 certified, including Nissan, Ford, and IBM. (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, nether CC BY iv.0 license)
Another type of sustainability standard with which businesses may elect to comply is LEED certification. LEED stands for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, and it is a rating system devised past the U.S. Green Building Council to evaluate a structure'due south environmental performance. The about famous example is the Empire State Building in New York City, which was awarded LEED Gold condition (for existing buildings). The LEED certification was the result of a multimillion-dollar rebuilding program to bring the building up to date, and the edifice is the tallest in the United states to receive it. In that location are dozens of other examples of large commercial buildings, such as the Wells Fargo Tower in Los Angeles, likewise as thousands of smaller buildings and residential homes. LEED certification is the commuter behind the ongoing market transformation towards sustainable design in all types of structures, including buildings, houses, and factories.
The High Cost of Inaction
According to estimates from the EPA, by the year 2050, Earth's population will exist about x billion people. Dramatic population growth has had a very pregnant and frequently negative human impact on the planet. Not but are there more people to feed, house, and care for, but new technologies allow businesses to harness natural resource in unprecedented amounts. NGOs and government agencies alike have taken notice. For years, the Department of Land and the Department of Defense have considered climate modify to be a potential threat to the long-term security of the United states. If unmanaged, climate change could pose a risk to both U.Due south. security and Department of Defense facilities and operations.
Other respected organizations are besides alerting the public to the risks of ignoring climate change.
The Marriage of Concerned Scientists (UCS) has released a detailed report identifying approximately twenty serious risks that will be faced if the problem is non addressed in a substantial way. These risks include ascent seas and increased coastal flooding, more than intense and frequent oestrus waves, more than destructive hurricanes, wildfires that last longer and produce more impairment, and heavier precipitation in some areas and more severe droughts in other areas. In addition to extreme weather events, in that location would likely be widespread woods death in the Rocky Mountains and other mount ranges, the destruction of coral reefs, and shifts in the ranges of plants and animals. Both military bases and national landmarks would be at risk, as would the electrical grid and food supply. The UCS, with a membership consisting of the globe's most respected scientists, bases its projections on scientific enquiry studies that have produced empirical evidence of climate alter. Its official position is that "global warming is already having meaning and very costly effects on communities, public wellness, and our environment."
Ecology protection and climate change problems receive varying degrees of support at the national level, depending on the delivery unlike presidents make to them. During periods in which the assistants in Washington demonstrates a lower priority for climate change problems, such equally the Trump administration's announced intention to withdraw from the Paris Climate Accord, individual companies may accept the lead on actions to reduce global warming emissions.
For case, Microsoft founder Bill Gates recently announced the creation of a individual initiative to invest $20 billion on climate-related research and development over the next five years. This is an example of government-funded early experimental enquiry that a business may be able to plough into a commercially viable solution. If government steps dorsum, individual-sector companies concerned nigh long-term sustainability may accept to accept a leadership part.
Ultimately, it requires the cooperation of public and individual efforts to address climate change; otherwise, the impacts volition continue to intensify, growing more costly and more damaging."
Sustainability frequently requires the public and private sectors to cooperate. Inaction contributes to disasters like the 2017 devastation of Houston by Hurricane Harvey and of Puerto Rico by Hurricane Maria. There is often tension betwixt developers who desire to build and cities that effort to legislate for more light-green space. Greenish infinite non but offers a place for recreation and enjoyment of nature, but also provides essential natural drainage for rain and alluvion waters, reducing the likelihood that developed areas will stop up underwater in a storm.
Flooding in Houston: Is the Condition Quo Sustainable?
A symbiotic relationship exists betwixt development and flooding in urban areas such every bit Houston, Texas. Imagine yous are a member of the urban planning committee for the metropolis council of Houston, which recently suffered traumatic flood damage from several major storms, including Hurricanes Harvey and Ike, and Tropical Tempest Allison, all of which occurred since 2001 and acquired a total of approximately $75 billion in damages.
The floods also caused dozens of deaths and changed the lives of millions who lived through them. Future storms may increase in severity, because climate change is warming ocean waters.
The mayor and the city quango have asked the planning commission to advise specific solutions to the flooding problem. This solution must not rely exclusively on taxpayer funds and regime programs, but rather must include deportment past the private sector as well.
One of the nigh direct solutions is a seemingly simple tradeoff: The greater Houston surface area must reduce the percent of land covered by concrete while increasing the percentage of state dedicated to green space, which acts like a sponge to absorb flood waters earlier they can exercise severe damage. The planning commission thinks the best way to accomplish this is to issue a municipal ordinance requiring corporate developers and builders to set aside every bit dark-green infinite an amount of land at to the lowest degree equal to what volition be covered by physical, (neighborhoods, office buildings, parking lots, shopping centers). Nevertheless, this will increment the cost of development, because it ways more than land will be required for each type of project, and as a consequence, developers will have college country costs.
Critical Thinking
- Equally a fellow member of the urban planning commission, y'all will have to convince the stakeholders that a proposal to crave more dark-green space is a workable solution. Yous must become everyone, including developers, investors, neighborhood homeowner associations, politicians, media, and local citizens, on board with the idea that the benefit of sustainable evolution is worth the cost. What will you lot do?
- Is this a matter that should exist regulated past the local, land, or federal regime? Why?
- Who pays for flood damage after a hurricane? Are your answers to this question and the preceding one consistent?
U.South. government agencies, such as the National Aeronautics and Space Assistants (NASA) and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, accept identified many challenges in which sustainability tin make a positive contribution. These include climatic change, decreasing supplies of make clean h2o, loss of ecological systems, degradation of the oceans, air pollution, an increment in the utilize and disposal of toxic substances, and the plight of endangered species.
Progress toward solving these challenges depends in role on deciding who should aid pay for the protection of global environmental resources; this is an issue of both environmental and distributive justice.
1 fashion to accost the issue of shared responsibility betwixt corporations and society is the implementation of a "cap and trade" system. According to the Environmental Defense Fund, cap and trade is a viable approach to addressing climate change by curbing emissions that pollute the air: The "cap" is a limit on greenhouse gas emissions—if companies exceed their cap, they must pay penalties—whereas the "trade" allows companies to utilize the free market to buy and sell pollution allowances that permit them to emit a certain corporeality of pollution.
At nowadays, there are more than questions than answers, including how much of the responsibleness lies with governments, how this responsibility can be allocated betwixt adult and developing nations, how much of the toll should the individual sector bear, and how should these divisions of cost and responsibility exist enforced. Individual companies must carry office of the cost, and the business sector recognizes they take some responsibility, but many disagree on whether that should be in the class of subsequently-the-fact fines, or earlier-the-fact fees and deposits paid to the government. Regulations may very well have to be international in scope, or companies from i country may abuse the environs in another.
Is It Upstanding to Dump Toxic Waste material in Countries That Let It?
Should a multinational company accept reward of another land'south lack of regulation or enforcement if it saves money to do and so?
A New York Times news correspondent reporting from Nigeria constitute a collection of steel drums stacked behind a village's family living chemical compound. In this mid-1990s example, ten thousand barrels of toxic waste had been dumped where children alive, consume, and beverage.
As safety and environmental hazard regulations in the United States and Europe have driven toxic waste disposal costs up to $three,000 per ton, toxic waste brokers are looking for the poorest nations with the weakest laws, often in West Africa, where the costs might be closer to $3 per ton. The companies in this incident were looking for cheap waste-dumping sites, and Nigeria agreed to accept the toxic chemical waste matter without notifying local residents. Local people wearing shorts, t-shirts, and sandals unloaded barrels of polychlorinated biphenyls, placing them next to a residential area. Nigeria has oft been near the top of the United nations' list of almost corrupt nations, with government leaders cutting deals to line their own pockets while exposing their citizens to environmental hazards.
A more contempo example occurred in Côte d'Ivoire (Republic of cote d'ivoire) in 2006, when residents discovered that hundreds of tons of "slops" (chemicals) from a foreign-owned send had been dumped near Abidjan, the country'southward commercial capital. The send was endemic by a multinational free energy visitor named Trafigura. According to a report from Amnesty International, more than than 100,000 residents were sickened, leading to 15 deaths. Trafigura had illegally dumped the toxic waste in Côte d'Ivoire later on searching for a disposal site in several other countries.
Critical Thinking
- Should a U.S. or European company take advantage of a country'south weak approach to business and political ethics?
- Would your answer change if your decision saved your company $ane million?
Inaction on issues of sustainability can lead to long-term environmental consequences that may not exist reversible (the death of ocean coral, the melting of polar ice caps, deforestation). Another hurdle is that it is sometimes difficult to convince companies and their investors that quarterly or annual profits are short-term and transitory, whereas ecology sustainability is long-term and permanent.
Ecology Economics and Policy
Some politicians and business leaders in the United States believe that the U.S. system of capitalism and free enterprise is the main reason for the nation'south prosperity over the by two hundred years and the primal to its future success. Free enterprise was very effective in facilitating the economic development of the United States, and many people benefited from it. Simply it is equally true that this could not have happened without the country'south wealth of natural resources like oil, gas, timber, h2o, and many others. When we consider the environment and the function of sustainability, the question is not whether our system works well with an abundance of natural resource. Rather, we should enquire how well information technology would work in a nation, indeed in a globe, in which such resources were severely limited.
Does business, as the prime number user of these resources, owe a debt to order? The Harvard Business concern Review recently conducted a debate on this topic on its stance/editorial pages. Concern owes the world everything and nothing, according to Andrew Winston, author and consultant on environmental and social challenges. "It'southward an important question," he wrote, "but i that implies business should exercise the socially responsible matter out of a sense of duty. This thought is a distraction. Sustainability in business is not virtually philanthropy, but about profitability, innovation, and growth. Information technology's merely apparently good business."
On the other hand, Bart Victor, professor at Vanderbilt University's Owen Graduate School of Management, wrote, "Business organization is far more powerful and deeply influential than any competing ideological force, political forcefulness or ecology force . . . business now has to see itself and its responsibilities and obligations in a new fashion."
Using deontological or duty-based reasoning, we might conclude that business does owe a debt to the environment. A basic moral imperative in a normative arrangement of ethics is that someone who uses something must pay for it. In contrast, a more than utilitarian philosophy might concur that corporations create jobs, make coin for shareholders, pay taxes, and produce things that people want; thus, they have done their part and practice not owe any other debt to the environment or guild at large. Notwithstanding, utilitarianism is often regarded equally a "here and now" philosophy, whereas deontology offers a longer-term approach, taking future generations into account and thus adjustment more with sustainability.
Should businesses take to pay more than in fees or taxes than ordinary citizens for public resource or infrastructure they use to make a profit? Consider the example of fracking: W Texas has seen a recent boom in oil and gas drilling due to this relatively new process. Fracking is curt for hydraulic fracturing, which creates cracks in rocks beneath Earth'south surface to loosen oil and gas trapped in that location, thus allowing it to flow more than easily to the surface. Fracking has led to a greatly expanded try to drill horizontally for oil and gas in the The states, especially in formations previously thought to be unprofitable, considering there was no viable way to get the fossil fuels to the surface. Nevertheless, information technology comes with a significant downside.
Fracking requires very heavy equipment and an enormous amount of sand, chemicals, and water, most of which must be trucked in. Traffic effectually Texas's small towns has increased to ten times the normal corporeality, buckling the roads under the pressure of a never-ending stream of oil company trucks. The towns do not have the budget to repair them, and residents end upwards driving on dangerous roads full of potholes. The oil visitor trucks are using a public resources, the local road organisation, oft congenital with a combination of land and local taxpayer funds. They are obviously responsible for more than of the damage than local residents driving four-door sedans to piece of work. Shouldn't the businesses have to pay a special levy to repair the roads? Many recall it is unfair for small towns to have to burden their taxpayers, most of whom are not receiving any of the profits from oil and gas development, with the cost of road repair. An alternative might be to impose a Pigovian tax, which is a fee assessed confronting individual businesses for engaging in a specific activity (proposed by British economist A. C. Pigou). If set at the proper level, the revenue enhancement is intended as a deterrent to activities that impose a net price—what economists call "negative externalities"—on third parties such every bit local residents.
This issue highlights ane of many environmental debates sparked by the fracking process. Fracking also causes the overuse and pollution of fresh water, spills toxic chemicals into the basis water, and increases the potential for earthquakes due to the injection wells drilled for chemical disposal. Ultimately, as is oftentimes the instance with issues stemming from natural resource extraction, local residents may receive a few brusk-term benefits from business activeness related to drilling, just they end upward suffering a asymmetric share of the long-term damage.
One method of dealing with the long-term harm caused by pollution is a carbon tax, that is, a "pay-to-pollute" organisation that charges a fee or revenue enhancement to those who discharge carbon into the air. A carbon tax serves to motivate users of fossil fuels, which release harmful carbon dioxide into the atmosphere at no price, to switch to cleaner free energy sources or, declining that, to at least pay for the climate harm they crusade, based on the amount of greenhouse gas emissions generated from burning fossil fuels. A proposal to implement a carbon tax system in the U.s. has been recommended by many organizations, including the conservative Climate Leadership Council (CLC).
Exxon Mobil, Beat out, British Petroleum, and Total, forth with other oil companies and a number of large corporations in other industries, recently announced their support for the plan to tax carbon emissions put forth by the CLC.
Visit the Carbon Taxation Center to learn well-nigh the carbon revenue enhancement as a monetary disincentive.
Would this "pay-to-pollute" method really work? Will companies agree to repay the debt they owe to the environment? Michael Gerrard, the director of the Sabin Center for Climate Change Law at Columbia University Law School, said, "If a sufficiently high carbon tax were imposed, it could accomplish a lot more for fighting climate change than liability lawsuits."
Initial estimates are that if the programme were implemented, companies would pay more than $200 billion a twelvemonth, or $ii trillion in the first decade, an corporeality accounted sufficient to motivate the expanded apply of renewable sources of free energy and reduce the employ of nonrenewable fossil fuels.
Some ecology organizations, including the Nature Salvation and the World Resource Institute, are also endorsing the program, as are some legislators in Washington, DC. "The bones idea is simple," Senator Sheldon Whitehouse (D-RI) said. "Yous levy a toll on a thing you lot don't desire—carbon pollution—and you apply the revenue to help with things y'all do want."
According to the senator, a U.Southward. carbon tax or a fee of $45 per metric ton would reduce U.S. carbon emissions past more than 40 percent in the first decade. This is an idea with global support, and it has already been tried. The World Bank has information indicating that forty countries, along with some major cities, have already enacted such programs, including all countries of the EU, every bit well as New Zealand and Nippon.
Corporate and Personal Choices Regarding the Environment of the Futurity
The car manufacturer Tesla is developing new technologies to allow people to reduce their carbon footprint. In addition to a line of electric cars, the visitor makes other renewable energy products, such as roofing tiles that human action as solar energy panels, and promotes longer-term projects such as the Hyperloop, a high-speed train projection jointly designed past Tesla and SpaceX.
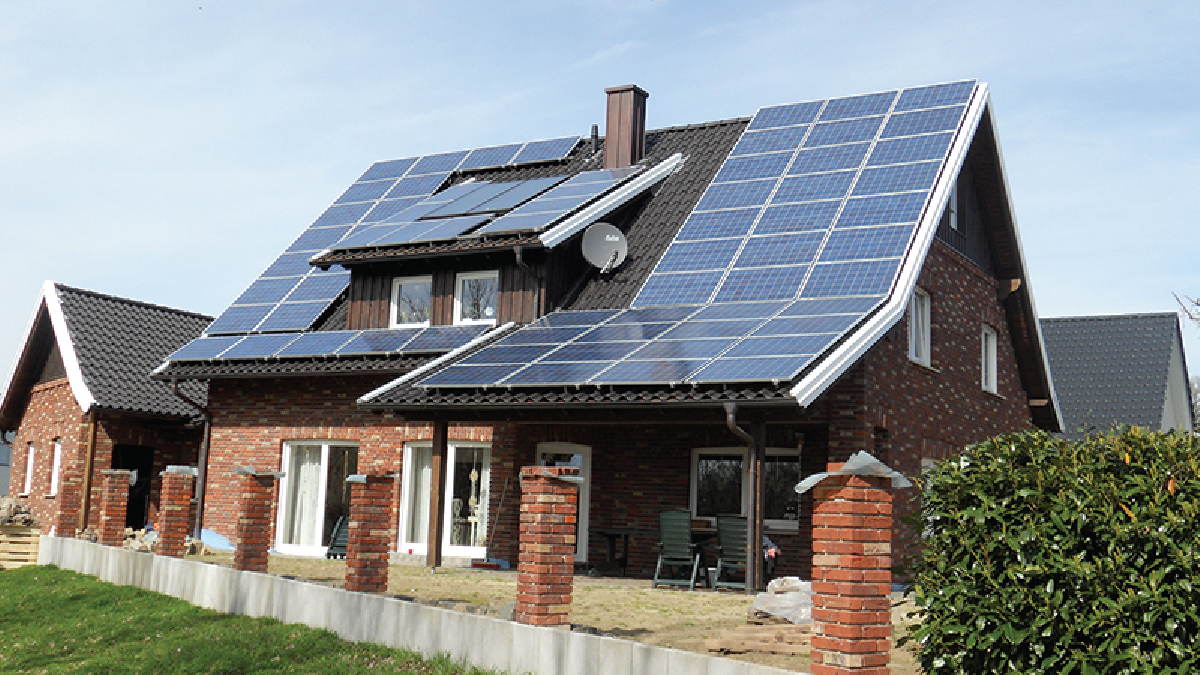
Of course, if businesses are to succeed in selling environmentally friendly products, they must accept consumers willing to purchase them. A homeowner has to exist prepare to spend xx percentage more than than the cost of a traditional roof to install solar roofing tiles that reduce the consumption of electricity generated by fossil fuels ((Figure)).
Although solar panels can reduce your carbon footprint, the tiles are much more expensive than standard covering tiles. (credit: "Typical Solar Installation" by Tim Fuller/Flickr, CC By two.0)

Another personal decision is whether to buy a $35,000 Tesla Model 3 electric motorcar. While it reduces the driver's carbon footprint, it requires charging every 250 miles, making long-distance travel a challenge until a national system of charging stations is in place.
Tesla's founder, Elon Musk, is also the founder of SpaceX, an aerospace manufacturer that produces and launches the only infinite-capable rockets currently in existence in the United States. Thus, when NASA wants to launch a rocket, it must do so in partnership with SpaceX, a private visitor. Information technology is often the case that individual companies develop important advances in technology, with incentives from government such every bit tax credits, depression-involvement loans, or subsidies. This is the reality of uppercase-intensive, high-tech projects in a free-market economy, in which authorities spending may be limited for budgetary and political reasons. Non only is SpaceX making the rockets, but information technology is making them reusable, with long-term sustainability in mind.
Critical Thinking
- Should corporations and individual consumers carry joint responsibility for sustaining the environment? Why or why not?
- What obligation does each of usa take to be aware of our own carbon footprint?
- If private consumers accept some obligation to support environmentally friendly technologies, should all consumers bear this responsibility as? Or just those with the economic means to do so? How should order determine?
Summary
Adopting sustainability as a strategy means protecting the environment. Order has an involvement in the long-term survival, indeed the flourishing, of ecological habitats and natural resources, and we ask and expect companies to respect this societal goal in their business activities.
When analyzing what a business owes gild in return for the freedom to extract our natural resources, we must residuum development and preservation. It may be piece of cake to say from afar that a business should cut back on how much information technology pollutes the air, only what happens when that means cutting back on fossil fuel utilize and transitioning to electric vehicles, a pick that affects anybody on a personal level?
Assessment Questions
What is globe jurisprudence?
Globe jurisprudence is an estimation of law and governance based on the belief that guild will exist sustainable only if nosotros recognize the legal rights of Earth as if it were a person.
Which of the following best describes the tragedy of the eatables?
- People are always willing to cede for the proficient of social club.
- People are probable to use all the natural resources they want without regard to others.
- The common adept of the people is a popular corporate goal.
- Tragedies occur when there is too much government regulation.
B
ISOs are sustainability standards for businesses ________.
- promulgated by the land government
- promulgated by the federal government
- promulgated by the Globe Trade Organization
- none of the higher up
D
True or false? If environmental harm is discovered, the business concern entity causing it is frequently held liable by both the authorities and the victims of the harm in carve up proceedings.
True
Which of the following is a potentially constructive manner to reduce global warming?
- build more than coal-burning power plants
- build more diesel fuel-called-for cars
- implement a carbon tax
- implement taxation-complimentary gasoline
C
Endnotes
19H.J. Graham, Lowest's Constitution. (Madison: State Historical Social club of Wisconsin, 1968). See also H.J. Graham, "The 'Conspiracy Theory' of the Fourteenth Amendment," Yale Police force Periodical 47, no. three (1938): 341–403. doi: ten.2307/791947.
xx"Ecuador Adopts Rights of Nature in Constitution," The Rights of Nature. https://therightsofnature.org/ecuador-rights/.
21 M. Triassi, et al., "Environmental Pollution from Illegal Waste matter Disposal and Health Effects," Int J Environ Res Public Health 12, no. two (2015): 1216–1236. doi: ten.3390/ijerph120201216.
22Gwynn Guilford, Quartz, Dec ix, 2014. https://qz.com/308970/cruise-ships-dump-i-billion-tons-of-sewage-into-the-sea-every-year/.
23State of the World 2010 Transforming Cultures from Consumerism to Sustainability. Washington, DC: The Worldwatch Institute, 2010.
24Rights of Nature, "Principles of Globe Jurisprudence." https://therightsofnature.org/principles-of-earth-jurisprudence/.
25Garrett Hardin, "The Tragedy of the Eatables," Science 162, no. 3859 (1968): 1243–1248. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3859.1243.
26Jeff Kauflin, "The World's Most Sustainable Companies 2017," Forbes, January 17, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/jeffkauflin/2017/01/17/the-worlds-virtually-sustainable-companies-2017/#2773f73a4e9d.
27Corporate Knights, "2018 Global 100." http://www.corporateknights.com/reports/global-100/.
28Jeff Kauflin, "The Earth's Near Sustainable Companies 2017," Forbes, January 17, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/jeffkauflin/2017/01/17/the-worlds-most-sustainable-companies-2017/#2773f73a4e9d.
293BLMedia, "2015 Cisco Corporate Social Responsibleness Report: Supply Chain," 2015. http://3blmedia.com/News/2015-Cisco-Corporate-Social-Responsibility-Study-Supply-Chain.
30McKinsey & Co., "Sustainability's Strategic Worth," 2016. http://csr-raadgivning.dk/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Sustainabilitys-strategic-worth-McKinsey-Global-Survey-results-McKinsey-July-2014.pdf.
31Paul Raleigh, "Corporate Social Responsibility: Across Financials," Grant Thornton, August 13, 2014. https://www.grantthornton.global/en/insights/articles/Corporate-social-responsibleness/.
32Jessica Lyons Hardcastle, "Dell's Flexible Work Programs Save $12M, Reduce GHGs," Environmental Leader, July 10, 2014. https://www.environmentalleader.com/2014/07/dells-flexible-work-programs-salvage-12m-reduce-ghgs/.
33Knut Haanaes, "Making Sustainability Profitable," Harvard Business organisation Review, March 2013. https://hbr.org/2013/03/making-sustainability-profitable.
34Adam Wernick, "The U.South. Defense Department Takes Climate change Seriously," Public Radio International, October eight, 2017. https://www.pri.org/stories/2017-x-08/usa-defense-department-takes-climate-modify-seriously.
35Union of Concerned Scientists, "Global Warming Impacts." https://www.ucsusa.org/our-work/global-warming/science-and-impacts/global-warming-impacts#.WjQa11WnF0w.
36Lucy P. Marcus, "Why Stiff Ties between Business and Government Affair," The Guardian, January 4, 2016. https://world wide web.theguardian.com/business/2016/jan/04/why-potent-ties-betwixt-business-and-government-matter-r-and-d.
37Union of Concerned Scientists, "Global Warming Impacts." https://www.ucsusa.org/our-piece of work/global-warming/scientific discipline-and-impacts/global-warming-impacts#.WjQa11WnF0w.
38National Conference on Country Legislatures, "State Plastic and Paper Bag Legislation," July 5, 2017. http://www.ncsl.org/research/environment-and-natural-resource/plastic-bag-legislation.aspx.
39Elizabeth Chuck, "Hurricane Harvey: How Many Billions of Dollars in Impairment Will Celebrated Storm Cost?" NBC News, Baronial xxx, 2017. https://www.nbcnews.com/storyline/hurricane-harvey/how-many-billions-impairment-will-harvey-cost-s-anyone-southward-n797521.
40NASA, "Study on Climate change," March 22, 2018. https://climate.nasa.gov/evidence/.
41James Brooke, "Waste Dumpers Turning to West Africa," New York Times, July 17, 1998. http://www.nytimes.com/1988/07/17/world/waste-dumpers-turning-to-westward-africa.html?pagewanted=all.
42Financial Transparency Coalition, "Cross-border Dumping of Hazardous Waste," August twenty, 2010. https://financialtransparency.org/hazardous-waste matter/.
43Andrew Winston, "Concern Owes the Globe Everything . . . and Nothing," Harvard Business organisation Review, May 4, 2010. https://hbr.org/2010/05/business-owes-the-world-everyt.html.
44Lew Harris, "Business concern Owes Pregnant Obligations to Order," Newswise, February 23, 2000. https://www.newswise.com/manufactures/business organisation-owes-meaning-obligations-to-society.
45Climate Leadership Quango, "The Four Pillars of Our Carbon Dividends Plan." https://world wide web.clcouncil.org/our-plan/.
46John Schwartz, "Exxon Mobil Lends Its Support to a Carbon Revenue enhancement Proposal," New York Times, June 20, 2017. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/06/twenty/science/exxon-carbon-tax.html.
47John Schwartz, "Exxon Mobil Lends Its Support to a Carbon Tax Proposal," New York Times, June 20, 2017. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/06/20/science/exxon-carbon-tax.html.
48Katy Lederer, "Why Can't Republicans Back up a Carbon Tax?" The New Yorker, Nov 9, 2015. https://world wide web.newyorker.com/business/currency/why-deceit-republicans-back up-a-carbon-taxation.
Glossary
- cap and trade
- a organization that limits greenhouse gas emissions past companies while allowing them to buy and sell pollution allowances
- carbon footprint
- the amount of carbon dioxide and other carbon compounds released past the consumption of fossil fuels
- carbon tax
- a pay-to-pollute system in which those who discharge carbon into the air pay a fee or revenue enhancement
- corporate personhood
- the legal doctrine holding that a corporation, separate and apart from the people who are its owners and managers, has some of the aforementioned legal rights and responsibilities enjoyed by natural persons
- sustainability
- a long-term approach to the interaction between business concern activeness and societal bear on on the surround and other stakeholders
- tragedy of the commons
- an economy theory highlighting the human tendency to use as much of a free natural resource equally wanted without regard for others' needs or for long-term ecology effects or issues
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/businessethicsopenstax/chapter/sustainability-business-and-the-environment/
0 Response to "what stance do firms who do as little as possible to solve social or environmental problems take"
Post a Comment